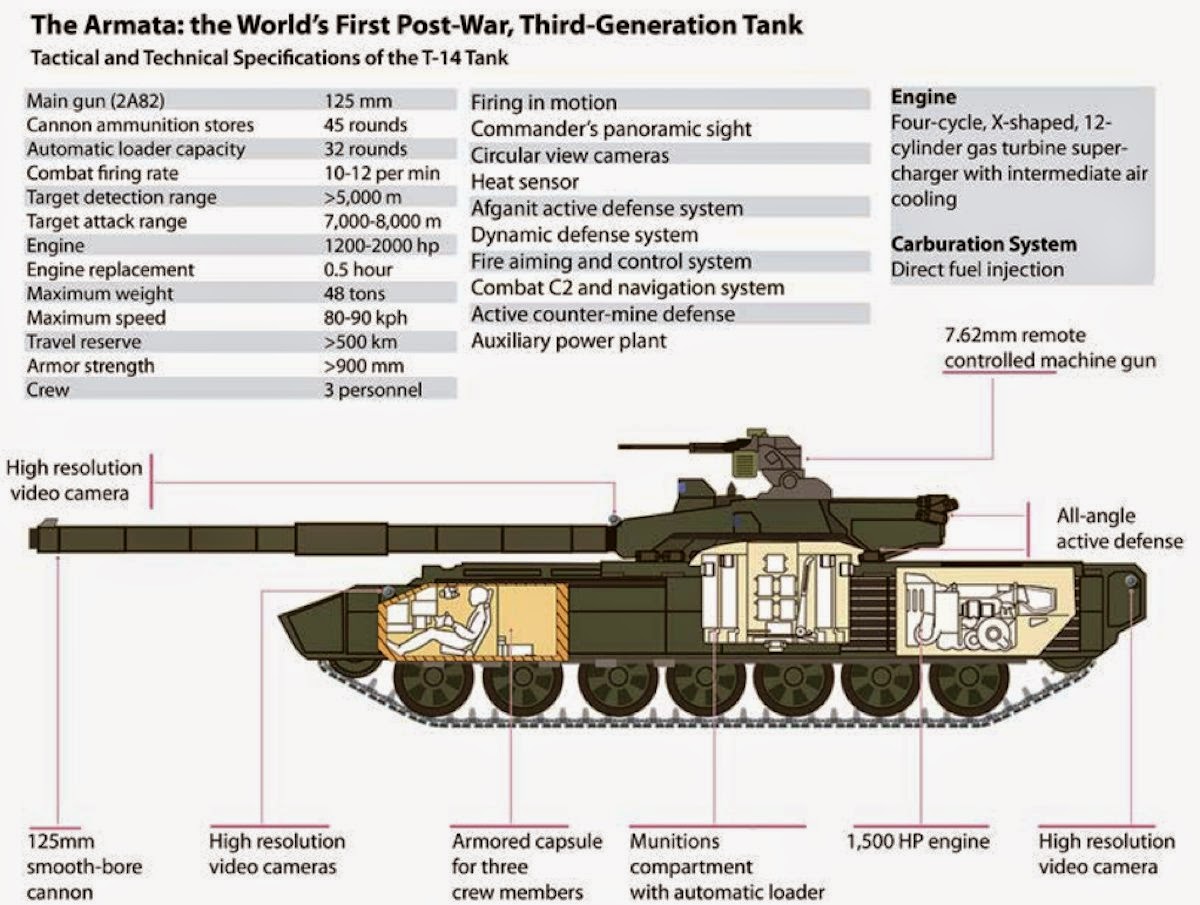
Large-scale deliveries of the new tanks and infantry vehicles are possible in 2017-2018. The advanced T-14
tank, a heavy infantry vehicle and an armored evacuation vehicle are being designed on the basis of Armata.
The tank’s main armament is the 2A82 125-mm smoothbore cannon, capable of firing high-powered munitions, including armor-piercing discarding sabot, guided missile, shaped-charge, and other types of munitions.
The composite multilayered passive armor protection of the T-14 tank is built with steel made by electroslag remelting and is combined with new composites to protect the T-14 against the most advanced modern weaponry. The T-14 also has the Afganit active protection complex, capable of intercepting shaped-charged grenades, antitank missiles, and subcaliber projectiles.
The Armata’s active defense deserves special discussion. In fact this is an individual anti-missile and anti-projectile tank defense system. It defends the vehicle from strikes, including those from the air. Thus, even the most modern Apache helicopter will not have a 100 percent chance of destroying a T-14 with its missiles. Active defense is situated along the entire perimeter of the turret at various levels, which ensures complete protection of the tank’s most important elements.
The crew of three men is located in an armored capsule in the forward portion of the hull of the Armata.
According to the specialists, the forward projection has multilayered, combined armor protection which can withstand a direct hit of any type of rounds which exist today, [including] sub-caliber and cumulative rounds. In addition, the forward hemisphere is covered with an active defense system which is also able to intercept any type of antitank munition, including sub-caliber rounds, something previously believed to be impossible in principle.
The central compartment, where the ammunition stores are located, is protected in such a manner that it is not even threatened by grenadiers who have taken cover in basements. The lower side hemispheres around the turret are shielded by counter-missiles.
The engine and the motor and transmission compartment are located in the rear of the hull. The diesel is domestically manufactured and it has a rather unconventional construction. The published power is not less than 1,500 HP.
The hull is extended and it has seven drive wheels, which speaks to the fact that the tank is of an enhanced weight, possibly about 50 tons.
The combat information and control systems are constructed using modern digital technologies and domestically manufactured solid-state basic elements. The probability of hitting the target with the first shot is close to 100 percent. Constant monitoring of the status of vitally important elements is provided. This allows a possible malfunction to be predicted well before it occurs. This, in turn, significantly enhances the reliability and maintainability of the complex armored vehicle. The hull is amply provided with video cameras. They allow the crew to observe the situation all around the tank. If required, zooming can be switched on, and a distant object can be viewed in detail. Heat sensing and infrared viewing capabilities are also available under any weather conditions, day or night.
A video allegedly shows Russia’s brand new T-14 Armata tank. The Armata tank will be officially revealed to the public during the Victory Day parade on May 9.
It has the T-14’s seven wheel design and 125mm extended length smoothbore gun.
20 Armata units have been manufactured and issued to troops for practical training.
Armata tanks have been included in Russia’s 2015 defence order, with 2,300 to be ultimately deployed over several years.
SOURCES- RT.com, Youtube, US Army’s Foreign Military Studies Office

Brian Wang is a Futurist Thought Leader and a popular Science blogger with 1 million readers per month. His blog Nextbigfuture.com is ranked #1 Science News Blog. It covers many disruptive technology and trends including Space, Robotics, Artificial Intelligence, Medicine, Anti-aging Biotechnology, and Nanotechnology.
Known for identifying cutting edge technologies, he is currently a Co-Founder of a startup and fundraiser for high potential early-stage companies. He is the Head of Research for Allocations for deep technology investments and an Angel Investor at Space Angels.
A frequent speaker at corporations, he has been a TEDx speaker, a Singularity University speaker and guest at numerous interviews for radio and podcasts. He is open to public speaking and advising engagements.